In an exclusive interview with Telecom Review, Kamal Ballout, head of enterprise, MEA, Nokia highlighted how the COVID-19 pandemic paved the way for networks modernization and facilitated digital transformation. In addition, he explained more about Nokia Bell Labs Future X architecture and how it provides an intelligent and dynamic communications and cloud-based platform as the foundation for smart grids.
Do you think COVID-19 has presented an opportunity to modernize networks and work towards a more sustainable future?
Physical distancing and stay-at-home measures implemented during the pandemic have impacted the daily activities of utility personnel who operate and maintain electrical grids. These measures have also shifted demand from businesses to residences during the day. Utilities have adapted and performed exceptionally well, demonstrating effective preparedness and contingency planning.
The response to COVID-19 has increased awareness of the importance of safe, reliable power and its impact on everything we do. It has also shown that utilities must execute their digitalization plans to realize the benefits of Industry 4.0.
Digitalization is driving the need for better remote management and automation capabilities. These capabilities will be essential for utilities seeking to decarbonize their grids and efficiently provide reliable, high-quality power as they integrate more intermittent distributed renewable energy generation and storage.
Digitalization will also help utilities respond to shrinking demand and revenue by increasing efficiency and supporting business models that will help them thrive in the new energy future.
What are some of the advancements in digital automation technology that are facilitating the growth of the smart grid?
Automation and robotics in substations and low-voltage lines will reduce truck rolls and residential visits. Situational awareness technologies that use temperature sensors, cameras, geolocation, and smarter PPE will also find a new role. These technologies will rely on communications, AI, machine learning and industrial IoT.
New grid applications based on IP and multicast are on the rise. Synchrophasors let utilities take more frequent and precise measurements of the grid. Multicast capabilities provide cost effective communications for use of CCTV for grid monitoring and security and R-GOOSE for communicating substation events.
IP/MPLS is instrumental in enabling grid digitization and automation advancements. It meets the demands of today’s power grid and has replaced SDH and TDM networks. The IP layer integrated in IP/MPLS provides utilities with flexible network topologies, self-healing capabilities with multi-fault resiliency, and the freedom to hop on cellular and satellite links. IP/MPLS enables the latest applications, supports multicast for synchrophasors and CCTV, and can incorporate cybersecurity solutions. It also gives utilities full control over traffic engineering for network paths and eliminates the need for standalone IP routers inside substations.
IP/MPLS can be extended to devices at the grid edge over a private LTE network. This reduces OPEX by providing utilities with one service, management, and security environment for all grid operations.
Technologies that track workers’ locations and understand the tasks can help utilities improve situational awareness and safety. For example, cameras and sensors connected with private LTE networks can ensure that utilities know where workers are and where hazards exist. Analytics systems powered by AI and machine learning can analyze sensor and CCTV data and raise alerts in real time. Smart PPE can warn workers about threats and communicate with central operations software to trigger an effective response.
Low-latency, high-bandwidth private LTE or 5G networks create new service opportunities for power utilities. For example, they can enable utilities to maintain DER assets or microgrids for hospitals or plant facilities. If households need reliable power for medical equipment, a utility could offer an enhanced response without sending personnel to the premises.
How is Nokia facilitating the digitization of power utilities?
The challenges of COVID-19 and digitalization drive a set of needs shown on the left of the figure below. The right side of the figure shows the Nokia Bell Labs Future X architecture for power utilities, which will enable utilities to use their existing communications investments to address these needs.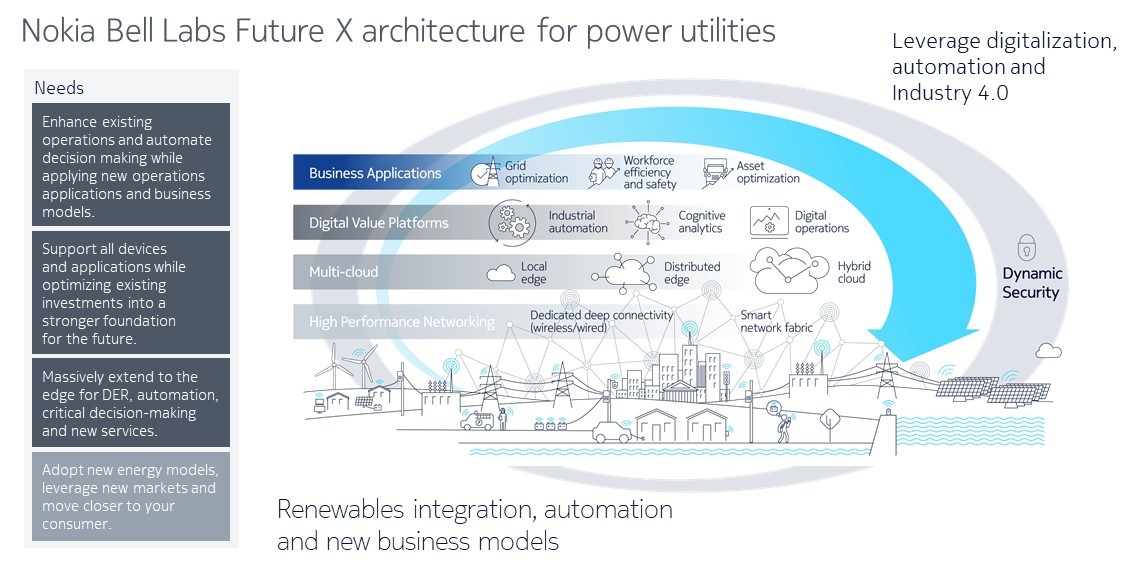
The Future X architecture provides an intelligent and dynamic communications and cloud-based platform as the foundation for smart grids. It will interconnect all systems, processes, and activities, and provide integrated analytics, machine learning and digital support for innovative new applications and services.
With the Future X architecture, power utilities can address any new demand, opportunity, or challenge with an agile and efficient network that can:
- Connect smart sensors, devices and mobile workers with the highest reliability and security
- Provide the high performance and ultra-low latencies required for automated wide area protection systems
- Increase network capacity where it’s needed for new applications while delivering deterministic performance for legacy systems such as teleprotection
- Use data from sensors and systems to improve distributed generation management, predict outages and maintain assets
- Apply analytics, sensor and device management, digital operations, and machine learning to any smart grid application
Can you tell us about any exciting projects or partnerships Nokia is involved in relation to developing the ecosystem for Industry 4.0?
Nokia is working with utilities everywhere to modernize and extend their communications networks as a foundation for Industry 4.0. In the Middle East and Africa, Nokia has been partnering with utility companies to help them install private LTE network based on 3GPP standards. They will use the network to implement IoT and automation use cases and provide smarter, faster service to its customers.
In the US, Nokia worked with the New York Power Authority (NYPA) to field-test connected drones for close-up inspections of power lines. NYPA operated the drones through a private LTE connection and monitored the drone camera feed in real time.
In Austria, Nokia and A1 are providing a private LTE network for a microgrid deployed at the Siemens headquarters in Vienna. The solution demonstrates how critical applications can be efficiently implemented and operated with secure, reliable, and fast connectivity.
Nokia’s private LTE focus includes industrial IoT solutions. A 2Q 2021 Guidehouse Insights report recognized Nokia as the market’s leading industrial IoT networking solution vendor.
COVID-19 has highlighted the critical role utilities play in the continuity of society. Fortunately, technologies such as LTE, 5G and IP/MPLS can provide a communications foundation for new Industry 4.0 capabilities that will make grids smarter, safer, and more reliable while realizing carbon reduction goals.
To find out more about how Nokia helps power utilities succeed in the new energy future, visit https://www.nokia.com/networks/industries/power-utilities/.











