The annual IPv6 Enhanced Summit was held online on June 23, in its 3rd Middle-Eastern edition, with international and regional industry experts who gave insightful keynotes on the online summit’s main theme “IPv6 Enhanced: Inspiring Innovation, Boosting Middle East Digitalization”.
Toni Eid, Founder of Telecom Review Group and CEO of Trace Media, who was the moderator and MC, welcomed the speakers and gave an overview on the online summit’s main topics and points of discussions. He then gave the floor to the first speaker, Dr. Bilel Jamoussi, Chief of Study Groups Department, ITU TSB.
IPv6 Enhanced for National Development
Entitled “IPv6 Enhanced for National Development”, his presentation focused on the importance of the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 and the different country status.
According to Jamoussi, 5G deployment is accelerating, which requires a significant number of addresses for the massive pipe connectivity, to connect the Internet of Things devices, “The IPv4 address space has been depleted, so there is a need to go from IPv4 to IPv6.”
“There is a high demand for IP addresses, at the same time, there’s a total depletion of the V4 space around the world, thus this puts the IPv6 at the forefront of policymaking, then the technology transition and capacity building”, he said.
“At ITU we have a number of resolutions agreed by 193 member states of the ITU from the private sector and other stakeholders that tackled the importance of IPv6 deployment.
These are important instruments to make sure that the transition from v4 to v6 is at the highest level. According to Dr. Jamoussi, policymakers, ministers of ICTs, and regulators of ICTs are the decision-makers who have the power to accelerate this transition.
ITU also accompanies the member states who wish to do this transition. “We have an accompaniment project to help build the capacity, along with our partners in the regional internet registries and other stakeholders to make sure that the engineers that used to deploy only IPv4 networks are now capable of deploying, managing, and running the IPv6.”
UAE Government IPv6 Policies and Strategy
One of the keynotes addressed during the 3rd Middle East IPv6 Enhanced Online Summit tackled the UAE government’s IPv6 policies and strategy. Eng. Meshal Al Mheiri, Manager - Digital Policies Development, Telecommunications and Digital Government Authority (TDRA) shared a comprehensive presentation discussing the importance of IPv6; the current status of IPv6 in the UAE; risks and challenges of transitioning; the transformation deployment plan; and the stakeholders involved in the IPv6 journey.
“We are in the time where we need to enhance the adoption of IPv6 within our country, with the support of different countries to achieve the highest adoption rate,” said Al Mheiri. With IPv6 being adopted worldwide, this internet protocol enhancement is already part of the present, and not the future.
Highlighted by TDRA, IPv6 brings simplified and more efficient routing, end-to-end (E2E) encryption for all connections, auto-configuration and mobility, and has built-in authentication and privacy support.
Al Mheiri pointed out that IPv4 was fully allocated in 2011, with 3.7 billion usable addresses. But with the growing dependence on connected devices and IoT, there’s an increased need for a large number of addresses. Google IPv6 data has shown that, as of June 17, 2022, there has been a 39.52% native adoption of IPv6 around the world.

Globally, India, Belgium, Malaysia, France, and Germany are leading the IPv6 adoption race while in the Middle East, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are prominent. Al Mheiri described that the adoption rate in the region can be categorized as either low or mid-to-high.
Current status of IPv6 in the UAE
Al Mheiri confirmed that there is a steady growth in the adoption rate of IPv6 in the country during Q4 2021, and yet, the utilization remains to be low, recording less than 10% registered IPv6 addresses.
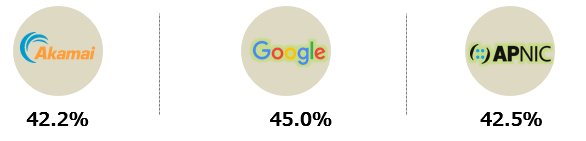
Based on leading content delivery network (CDN) providers Akamai, Google, and APNIC, the UAE’s conversion rate to IPv6 stands at 42.2%, 45%, and 42.5%, respectively. At present, there has been a 10% surge in these percentages.
Among the strategic importance of IPv6 in the UAE, Al Mheiri mentioned that the country needs about 35 million addresses, a huge difference to the around 4 million existing IPv4 addresses. Aside from that, IPv6 can also led to sustainable as well as modern and supportive infrastructure development, higher cybersecurity features, accelerated digital transformation, and more attractive ground for investments.
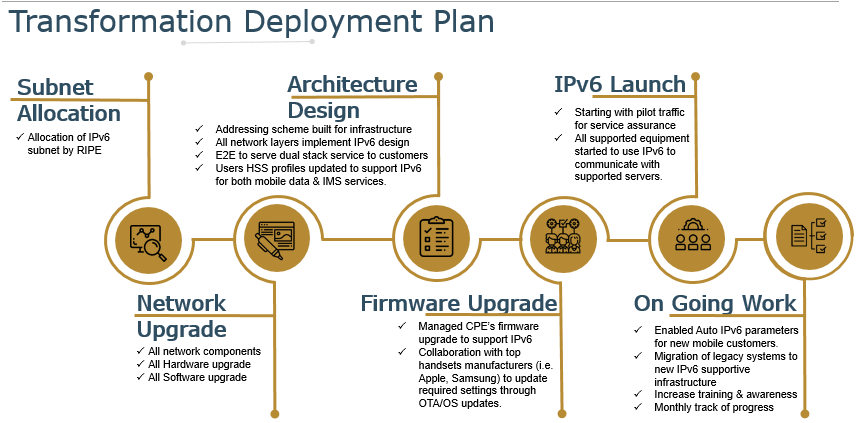
The UAE started the IPv6 deployment in 2009 on fixed broadband network, followed by mobile network in 2018. Starting from the allocation of IPv6 subnet by RIPE up to the architecture design and pilot traffic for service assurance, TDRA had to undergo network and firmware upgrade as part of its transformation deployment plan.
At the moment, “We have more automated IPv6 parameters to support any kind of new customers, being from a fixed or mobile network, to be registered with the parameters required to have a traffic initiated from there end-devices in the IPv6 cloud,” Al Mheiri expounded. They are also more focused on migrating legacy systems to avoid complexities and have smoother transformation towards the future of IPv6, while keeping track of ISPs’ progress on a monthly basis.

Accordingly, Al Mheiri emphasized that “the adoption of IPv6 is not an individual work, it’s a joint venture… Any country that would like to adopt IPv6 need to have a community, a complete chain that needs to be connected.”
In the UAE, TDRA, as the regulator, has partnered with local operators (Etisalat and du), CDN providers, manufacturers, and end-users for a holistic transformation.
Risks and challenges of transitioning
With all innovation comes risks and challenges, and these are present as well during UAE’s IPv6 transition. “Most of the organizations, particularly the ISP sector, from an infrastructure perspective, consider these challenges to transit from IPv4 to IPv6,” explained Al Mheiri.
Hardware lifecycle, higher costs with longer ROI, technical expertise, complex systems, and lack of user awareness are the challenges Al Mheiri stated on his presentation.
“Customers need to understand the benefits of transforming their home networks and business networks into an IPv6-enabled environment,” stressed Al Mheiri.
Despite these, the risks of not transitioning will entail increased cost, obstruction of smart city projects, interrupted cybersecurity measures, decreased service performance, and low investment opportunities.
Embrace IPv6 to Unleash Enormous Value
Xiaohong Yang, Project Manager - Information, Technology and Internet, Roland Berger presented on the social and economic benefits of IPv6 and IPv6 Enhanced (IPE). She categorized the benefits in three categories – sustainable economic growth by driving innovation and entrepreneurship, development of science and technology through promotion of emerging technologies, and improvement in peoples’ general well-being through enhanced IPv6 enabled applications.
“IPv6 is key to the essence of the free and open internet and it would empower digital economy transformation,” said Yang. “IPv6 could balance the digital power and provide equal access for all.”
She pointed out that IPv6 value creation is expected to reach $10.9 trillion in 2030 globally which translates to around 4.8% of all global real output. IPv6 high impact industries included information and communication, public service and utilities, hospitality and entertainment and professional services and finance, among others. “Application scenarios and business models, such as industry 4.0, smart manufacturing, 5G factories, etc, will lead to about 3.6 trillion value creation.”
She said that IPv6 will stimulate growth mainly via data security improvement, increase in efficiency and innovation empowerment. “New connections and in-depth innovation applications will garner almost 80% of the total sales enablements.” She pegged IPv6 enabled percentage of industry sales in 2030 of information and communication at 6.4%, public service and utilities at 5.9%, manufacturing at 5.8% and transport and storage at 5.6% among others.
In collaboration with Huawei, a by-value-chain method IPv6 deployment progress index for 2020 showed countries such as Belgium, Germany, Finland and India as front-runners; Norway, United Arab Emirates, China as adopters; and Chile, Venezuela and Lithuania as starters, among 79 countries.
Yang highlighted the discrepancies in core and user indicators and said IPv6 deployment at network core is crucial for country-wide adoption. She said that Roland Berger analysis shows that growth in IPv6 index can lead to GDP growth of a country. “For about every 10% increase in our IPv6 index, it resulted in about 0.4 increase in GDP.”
As an example of an adopter country, Yang cited Saudi Arabia. She said that CITC enabled IPv6 for public-facing services such as publish guidance to support private and government bodies in deploying IPv6. CITC also set up the National IPv6 Task Force in 2008. Yang stated that major operator stc enabled IPv6 on fixed network since 2015 and is leading 48% IPv6 deployment rate in the country.
In terms of policy recommendations for IPv6 deployment, Yang said that overall strategy could include creation of high level of IPv6 roll-out strategy in line with a roadmap with other digital strategies; creation of dedicated national taskforce, encouraging IPE pilot in telecommunication and government networks, and enhancing international collaboration on knowledge exchange. She also stressed on skills enablement and boosting of IPv6 awareness. Yang added that front-runner countries should take the next step toward driving IPE adoption and adopter and starter countries should leverage the recommended policies to further encourage the IPv6 and IPE deployment.
Latif Ladid, Founder and President of IPv6 Forum & Chair of ETSI ISG IPE explained in a pre-recorded video how IPv6 Enhanced drives digitalization and innovation.
Ladid discussed the importance of having an IPv6-only network, without having to carry 3 protocols at the same time. “We are moving to IPv6-only in certain domains. In the next 5 years, this will be an important step into getting IPv6 done which will give us a network control and facilitate configuration and maintenance of the network”, he said.
On IPv6’s impact on certain areas, he highlighted the influence on IoT, cloud computing and blockchain, while mentioning the need to protect data privacy and take into account data sovereignty. “It’s time to move to something faster and a lot cheaper”, he stated.
In his presentation, Latif Ladid explained how SRv6 is the cornerstone for smart connections in the 5G and cloud era and how it unleashes IPv6’s potential. He also emphasized that in the 5G and cloud era, IPv6 Enhanced is the key to improve service experience.
To wrap up, he gave an overview on ETSI ISG IPE and the latest releases it has done.
“We have 90 partners and members who have joined ETSI IPE from the five continents. The first release we have done is an analysis on the IPv6 Enhanced which has concluded that we’re on the right track. Also, IPE 5G Transport over IPv6 and SRv6 is under final review and is being tested by ISPs in Europe mainly. In addition, we’re also drafting the IPE Data Center and Cloud-Network Integration report.”
Etisalat IPv6 Adoption Journey
One of the keynotes addressed during the 3rd Middle East IPv6 Enhanced Online Summit tackled Etisalat’s IPv6 adoption journey.
Omar Almansoori, Vice President/Technology Acceleration, Etisalat UAE shared an insightful presentation discussing the operator’s IPv6 implementation journey; the challenges and pain points faced; and suggestions on what needs to be done to increase the IPv6 adoption.
Starting off his presentation from the beginning of their journey, Almansoori said, “We started in 2009, and of the main component we have to get is the IP addresses. We had 34 billion /64 subnets , and this would be sufficient in the long run”.
“Etisalat has a lot of integration points including GPON, business, access PE, packet core, etc. We had to put all these measures into deployment and upgrade all these components to support IPv6,” Almansoori explained.
Accordingly, the IPv6 addressing scheme was built from scratch, “putting a lot of consideration on prerequisites that we had,” Almansoori continued. The proposed IPv6 address allocation accommodates current and future customer requirements.
The allocation consideration was divided into several areas: internal, business, international, and mobile networks; Etisalat infrastructure, telecom services, and customer LAN/64; and future unallocated subnets.
Almansoori also laid out the main services within their IPv6 implementation journey. These include fixed broadband, mobile broadband, and business services. “Within each pillar are multiple components which have to be enabled with IPv6 support,” he described. “It sounds straightforward, but we need to make sure that those protocols are not only supporting the capabilities, but also you have to make sure that users don’t face issues during deployment.”
Following the actual implementation, the IPv6 traffic started to increase in May 2019. At the moment, 45-50% of Etisalat traffic is over IPv6, with Youtube, Facebook and Instagram videos, and Netflix as the leading applications utilizing it. As per Akamai, the Etisalat IPv6 traffic is 50.6% while the Google IPv6 for UAE, in general, is 44.78%.
To reach where they are today, some of the challenges Almansoori stressed are replicating all IPv4 network and security use cases/functions to work with IPv6; training staff for technical knowledge and practice; developing CPEs with various vendors; and aligning compatibility for all managed users.
To increase IPv6 adoption, Etisalat is focusing on two things: conducting customer awareness campaigns and approaching content delivery network (CDN) providers.
“We cannot approach every individual to replace their CPE. They have to adopt and acknowledge that they need IPv6 to improve credibility and performance of their connectivity,” Almansoori remarked. In comparison, IPv6 has better performance by almost 20% than IPv4.
EITC-du IPv6 Enablement and Future Prospects
Ali Alawadi, Head of Services Enablement, du gave a brief overview on du’s IPV6 enablement. He said that the means of communication were evolving from people-centric to machine-centric. “IPv4 helped us get where we are but it's no longer sufficient to take us where we want to be”, he said.
Alawadi said that from a telecom operator perspective, “IPV4 is today a rare commodity” and “with IPv6 we're removing that limitation in terms of numbers of the available resources,” he said. “There is a high necessity for the IPv6 to be rolled out and adopted as soon as possible.”
“Optimized costs, fewer network elements will ultimately lead to improved experience and improved performance,” he said.
He pointed out 4 key considerations for the evolution to IPv6 – Maintaining stable services during the evolution to IPv6, handset and device readiness for IPv6, know-how and awareness, and content provider adoption.
Highlighting du’s IPv6 deployment growth for provisioned subscribers, Alwadi said, “In 2021, we were only at 15%, and this year in June, we have jumped to 46% of our customers. He said that this could be achieved in a collaboration with the strong support of the regulatory body TDRA.
“As part of our journey based on our projection Q2 2023, we expect 100% of our customers to be fully provisioned with IPv6.”
Regarding the challenges in the IPv6 journey, Alwadi pointed out the following:
- Developing know-how and best practices for IPV6 rollout
- Upgrading the platforms and network elements that did not support the full capabilities of IPv4/IPv6
- Testing and validation of various integration points between IT and network systems for IPv6-related changes
- Handset and devices compatibility with IPv6
- Content providers' adaption of IPV6 (web applications)
- Prospects, unlimited possibilities IPV6 + PI and IPv6+ AI will bring industry innovation, experience assurance, and enormous connections
After his keynote, Toni Eid announced that EITC-du has joined the IPE organization and Dr. Will Liu, Vice-Chair of the IPE presented the official certificate.
EANTC and IPv6
Carsten Rossenhoevel, CTO and Co-Founder of EANTC, the European Advanced Networking Test Center in Berlin, Germany presented the latest SRv6 industry updates in a pre-recorded video.
As per Rossenhoevel, being an independent test lab, EANTC is running multivendor interoperability test events, focusing on transport technologies and application technologies in the fixed and mobile sector.
EANTC’s technical goals were to advance the multi-vendor interoperability of transport network solutions across the whole telco industry. In addition to SRv6 coverage, the center also covered SDN segment routing, NETCONF, EVPN services, flexible algorithm, FlexE, and clock synchronization.
According to Rossenhoevel, the building blocks for the success of SRv6 are the following:
- - Routing basics: BGP Global Routing Table, Route Summarization
- - Services: L3VPN, EVPN
- - Resiliency: Multi-Homing, Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA), Seamless BFD
- - Interworking: with MPLS, L3VPNs, with routed EVPN SR-MPLS, with EVPN over VXLAN
- - Constraint-Based Routing: FlexAlgo
Furthermore, Rossenhoevel added that “SRv6 is not going to substitute other types of transport networks completely anytime soon, and maybe that's also not even the goal. For this reason, Interworking is very important either with MPLS or with routed and switched EVPNs over a segment routing MPLS and over VXLAN.”
He also stated, “Constraint-based routing is a new trend which allows to automate slicing and quality-based routing and guarantee some constraints. An old topic but with a new type of solution.”
Lastly, Rossenhoevel concluded his intervention saying that “SRv6 is on a great path, and the technology is becoming more and more complete and more aligned with the other implementations of segment routing, over MPLS or VXLAN. The ecosystem continues to grow, more router vendors are supporting it, which also means that there are more ways to expand the network with different vendor integration.”
He also highlighted that during the EANTCs’s interoperability events, they intentionally only focus on functional testing. The areas that they still have to focus on in the future to close the gap to production networks are performance and scalability, in addition to energy efficiency and security aspects. These are important building blocks, which remain yet to be tested at a broader scale. However, “SRv6 is ready for primetime.”
At the end of the Online Summit, a poll was launched to know more about what the audience had to say about some of the IPv6 aspects and then a Q&A session followed.