In April 2019, South Korea launched a global-first 5G network, which has been adopted by KT Corporation. 5G networks have been delivered by at least 209 operators globally, spreading across 83 countries. 5G offers significantly improved performance over earlier network technologies such as 3G and 4G.
According to Ookla, they have looked at Speedtest Intelligence data by undergoing Speedtest results in the third quarter of 2022 to assess the following: how 5G performance has changed since last year; where download speeds are the fastest at the country level; and how satellite technologies are providing further connectivity options. They have also verified the countries where 5G isn't yet available to see where consumers are seeing improvements in 4G LTE access.
As of November 30, 2022, there were 127,509 5G deployments in 128 countries, up from 85,602 in 112 countries the previous year. Further, this year saw 5G speeds stabilize, with the median global 5G download speed hitting 168.27 Mbps in Q3 2022 as compared to 166.13 Mbps in Q3 2021.
Difference Between 4G and 5G
When compared to third-generation mobile networking, 4G enabled a previously unattainable quality of video streaming and calling on the go, meaning live TV is now routinely watched on the daily commute. However, increased video streaming has caused network congestion.
Chris Mills, head of industry analysis, at Tutela, has explained that the difference between 5G and 4G is that the network congestion will be eliminated in 5G because it will bypass the technical limits of 4G, greatly enhancing how much data can quickly transfer across blocks of spectrum.
In addition, under suitable conditions, 5G download speeds can reach 10 Gigabits per second, up to 100x faster than 4G, and reach the level of performance needed for an increasingly connected society. For instance, American telecommunication company AT&T’s 5G network can achieve download speeds of 75 Mbps, managing movie downloads in 49 seconds. The same on 4G can take up to an average of 50 minutes.
To summarize, the differences between 4G’s long-term evolution and the emergence of 5G basically come down to low latency, high speed and high density. This results in a higher number of connected devices and more capacity, the latter ensuring that much more data can be transferred from source to destination within a decreased timeframe and increased energy efficiency.
The Rank of the Fastest Download Speed by Using 5G in Different Countries
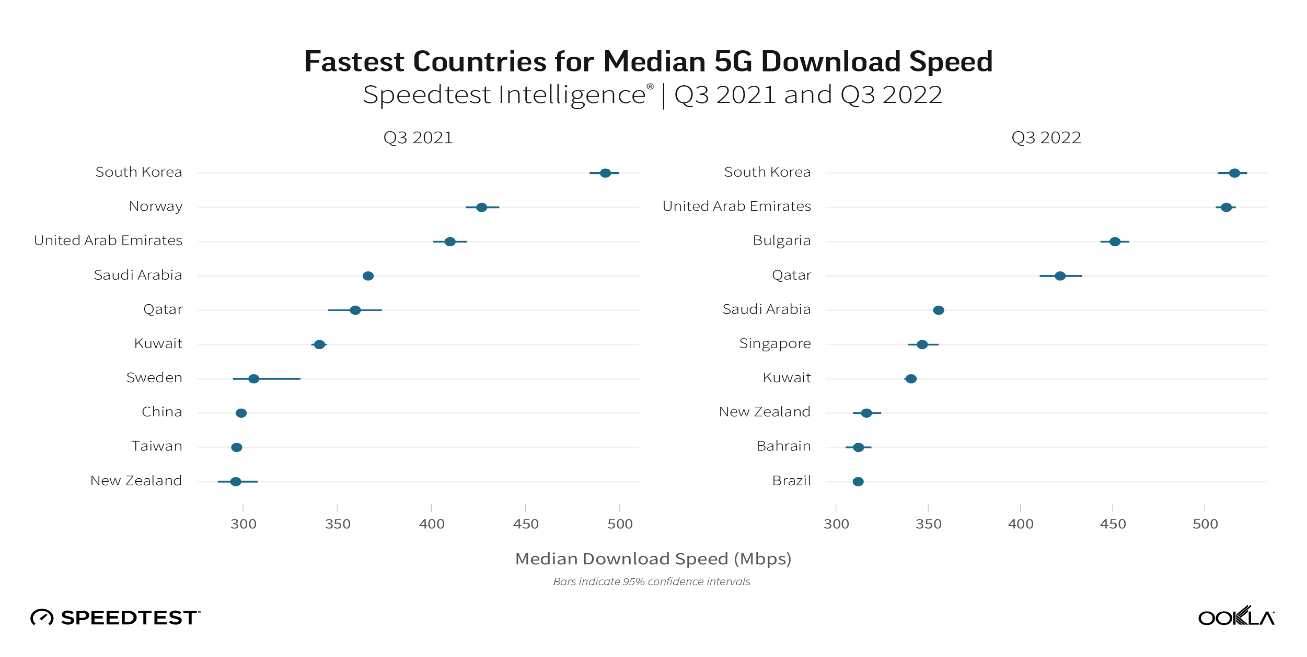
According to Ookla, South Korea and the United Arab Emirates have the fastest average download speeds on 5G in Q3 2022, with 516.15 Mbps and 511.70 Mbps, respectively, followed by Bulgaria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Kuwait, New Zealand, Bahrain and Brazil. Bulgaria, Singapore, Bahrain and Brazil are new to the top 10 for 2022, while Norway, Sweden, China and Taiwan have dropped out of the top 10.
Satellite Availability
In 2022, the satellite internet has seen a rapid expansion from Starlink, which is a satellite internet constellation operated by SpaceX and provides satellite Internet access coverage to many countries.
Starlink speeds have increased over the years, particularly in Canada and the United States. In the first quarter of 2022, Starlink reached the fastest satellite internet in Mexico, in North America; Lithuania, in Europe; Chile, in South America; and Australia, on the continent of Oceania.
Some countries were decreasing in the second and the third quarters of 2022, including Canada, France, Germany, New Zealand, the U.K. and the U.S.
5G Inaccessibility
Speedtest Intelligence found that more than 20% of the countries in the third quarter of 2022 had 2G and 3G connections that met the statistical threshold to be included (down from 70% in Q3 2021). These are primarily for the large portion of the population who are technologically behind and have to rely on decades-old technology that is sufficient for basic voice and text messaging, social media, and navigation apps — countries still eager for 5G. While it’s an improvement to see so many countries have been removed from this list, many 2G and 3G consumers remain hopeful that mobile operators will make 4G and 5G networks more efficient.
Future Vision of 5G
The future vision of 5G sees sustainability that meets the requirements of 1000x traffic growth. 5G will provide users with fiber-like data rates and a “zero” latency user experience. 5G will be able to connect 100 billion devices. 5G will be able to deliver a consistent experience in a variety of scenarios, including ultra-high traffic density, ultra-high connection density and ultra-high mobility. 5G will also provide intelligent optimization based on service and user perceptions, improving energy efficiency and cost efficiency by more than a hundred-fold.